:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/es/oido-medio/Yr6wekRlQtzWdYJMf6coiQ_oido_medio.png)
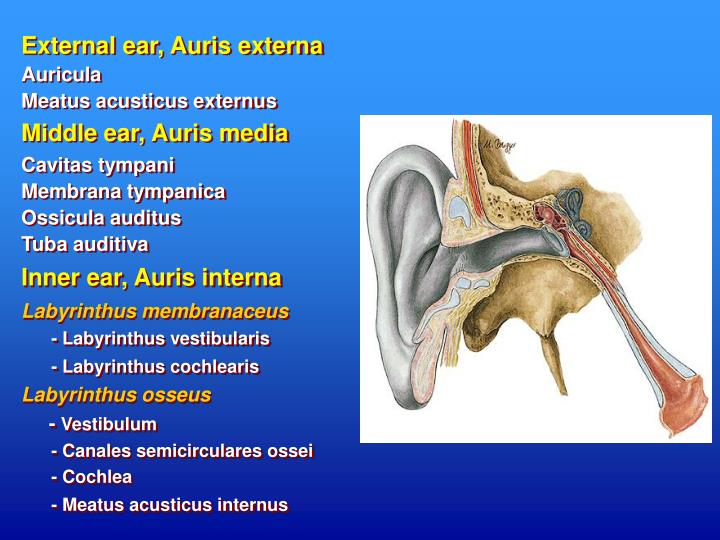
Oído medio Anatomía, partes, funciones Kenhub
The internal acoustic meatus was evaluated in 97 temporal bone specimens, half of which were radiographed in different projections.. Die Varianten des Meatus acusticus internus. Radiol. Diagn. 7 (1966), 141. PubMed. Google Scholar. 5. Camp J., Cilley.: The significance of asymmetry of the pori acustici as an aid in diagnosis of eighth nerve.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/internal-acoustic-meatus-2/4Ni2J0wKFABVnmVj2yZSQ_Meatus_acusticus_internus_02.png)
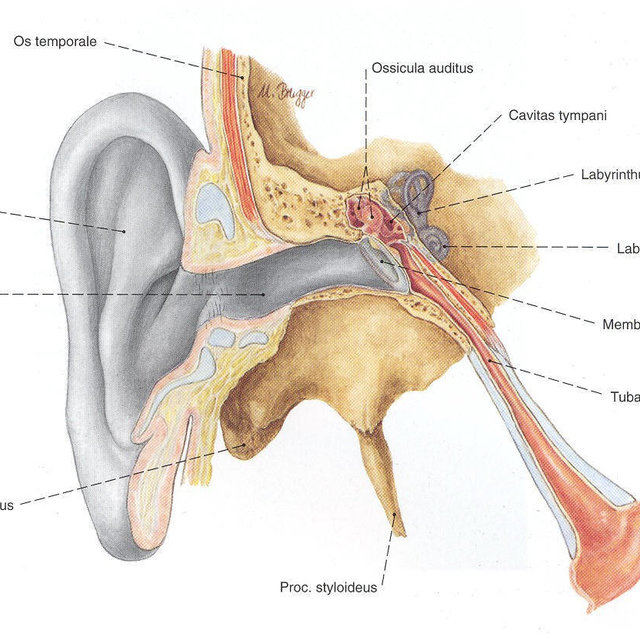
Innerer Gehörgang Anatomie und Klinik Kenhub
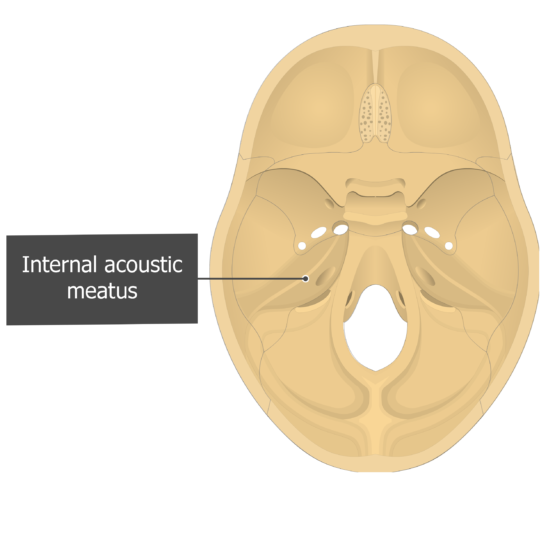
Internal acoustic meatus refers to a small bony foramen situated on the posterior surface of the petrous part of temporal bone, inside the posterior cranial fossa. It allows for the passage of three important structures, namely the vestibulocochlear nerve, facial nerve and the labyrinthine artery.
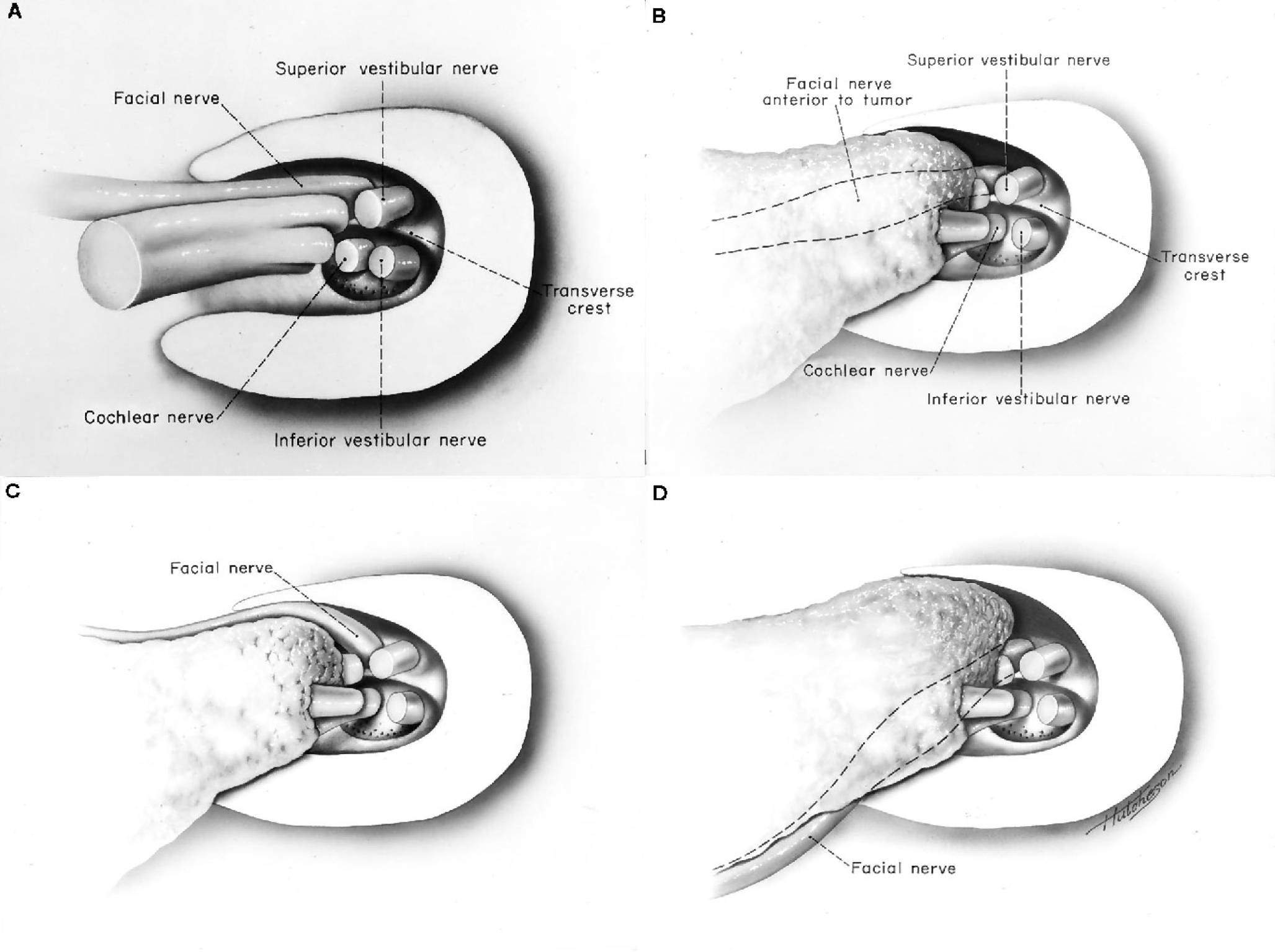
Cerebellopontine Angle and Cranial Nerves The Neurosurgical Atlas, by Aaron CohenGadol, M.D.
Meatus acusticus internus 1/6. Synonyms: Internal auditory canal, Canalis auditorius internus Clinical note Jugular foramen syndrome. Jugular foramen syndrome (JFS), also known as Vernet's syndrome is a disorder involving the palsies of the glossopharyngeal, vagus and accessory nerves (cranial nerves IX-XI), as well as sometimes the hypoglossal.

Internal Acoustic Meatus
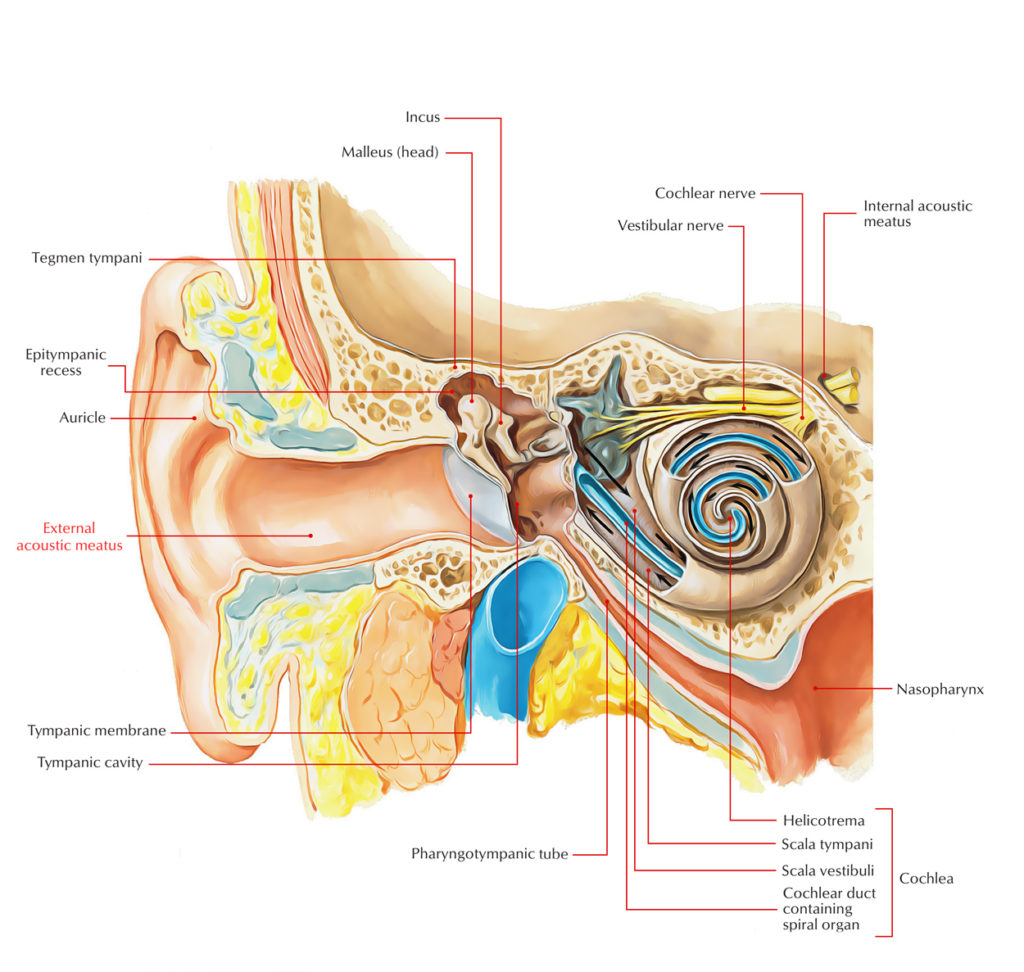
The internal auditory canal (IAC), also referred to as the internal acoustic meatus lies in the temporal bone and exists between the inner ear and posterior cranial fossa. It includes the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII), facial nerve (CN VII), the labyrinthine artery, and the vestibular ganglion..
External Auditory Meatus/Acoustic Meatus Earth's Lab
Der Meatus acusticus internus ist ein kleiner, relativ kurzer Knochenkanal, der im Felsenbein (Pars petrosa ossis temporalis) verläuft. Er beginnt am Porus acusticus internus und endet an einer durchlöcherten Knochenplatte, die an das Innenohr grenzt.
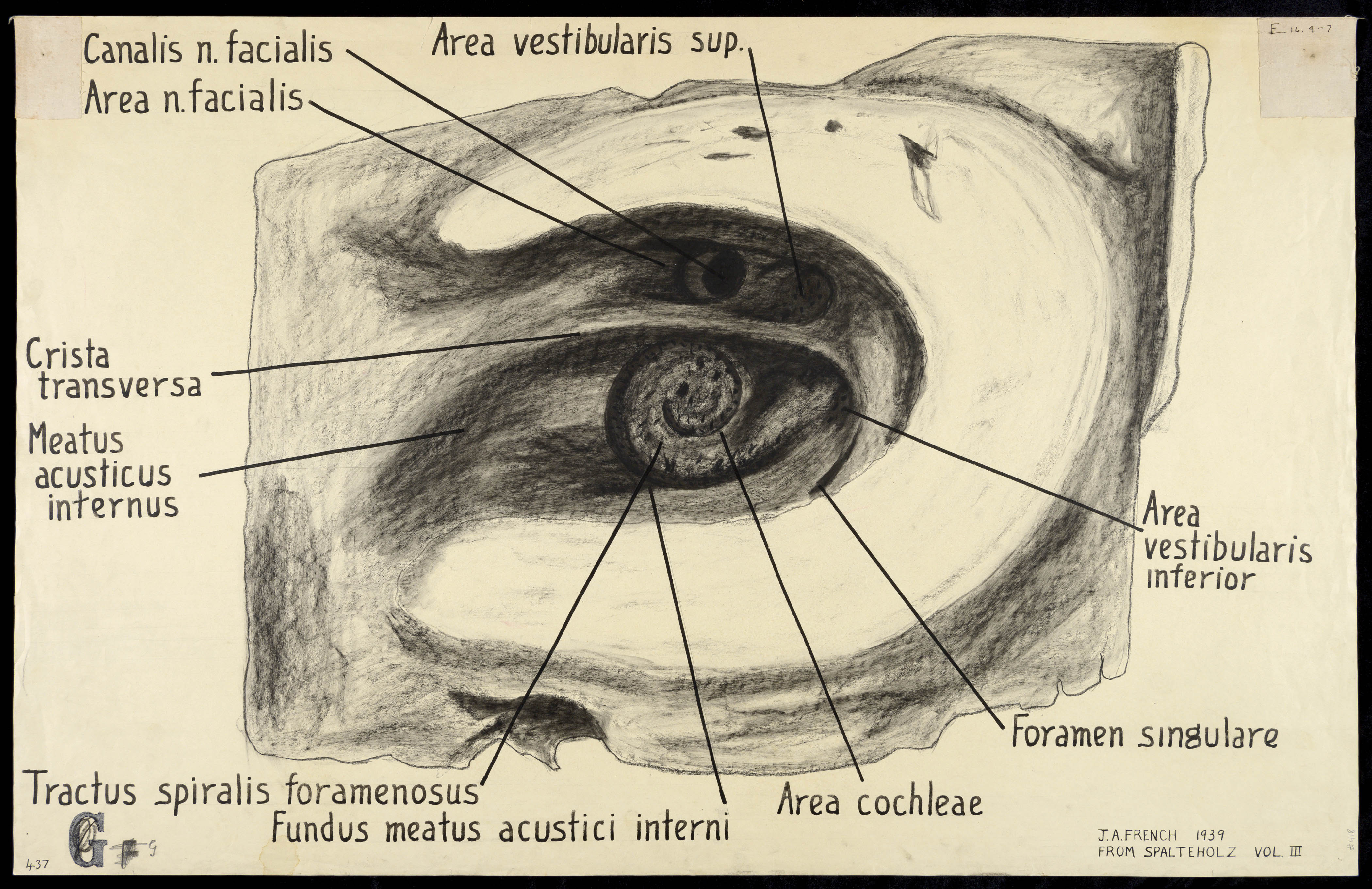
Canalis n. facialis, Area n. facialis, Crista transversa, Meatus acusticus internus...
The internal auditory meatus (also meatus acusticus internus, internal acoustic meatus, internal auditory canal, or internal acoustic canal) is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa and the inner ear . Structure

external acoustic meatus bone location
The internal acoustic canal (IAC) , also known as the internal auditory canal or meatus (IAM), is a bony canal within the petrous portion of the temporal bone that transmits nerves and vessels from within the posterior cranial fossa to the auditory and vestibular apparatus. Gross anatomy
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/meatus-acusticus-internus-2/Dv4LcHPPfyiGNfqccT7GQ_Meatus_acusticus_internus.png)
Pterygopalatine Fossa Anatomy and Contents Kenhub
The porus acusticus internus (plural: pori acustici interni), often merely referred to as porus acusticus, is the medial opening of the internal acoustic canal through which the facial nerve , vestibulocochlear nerve and labyrinthine artery pass 1 .
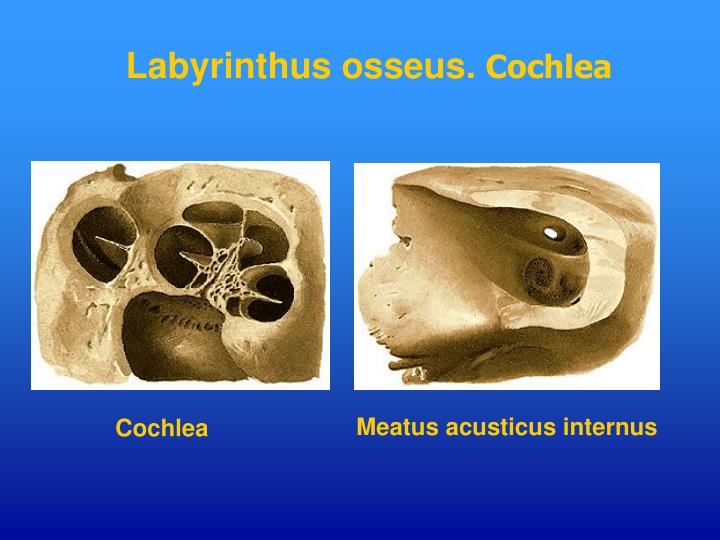
PPT Anatomy of the Ear PowerPoint Presentation ID6102402
MRI is firmly established as an essential modality in the imaging of the temporal bone and lateral skull base. It is used to evaluate normal anatomic structures, evaluate for vestibular schwannomas, assess for inflammatory and/or infectious processes, and detect residual and/or recurrent cholesteatoma. It is also extensively used in pre- and postoperative evaluations, particularly in patients.
external acoustic meatus bone location
meatus acusticus externus: MeSH: D004424: TA98: A15.3.01.045: TA2: 6867: FMA: 61734: Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about 2.5.
PPT Anatomy of the Ear PowerPoint Presentation ID6102402
Definition The internal acoustic opening is a large orifice near the center of posterior surface of petrous part, its size varies considerably; its margins are smooth and rounded, and it leads into a short canal, the internal acoustic meatus, about 1 cm. in length, which runs lateralward.

Meatus acusticus internus Ars Neurochirurgica
1. Background. The introduction of computerized transverse axial scanning (tomography) is a milestone in the development of applied radiology (1, 2).Quantitative and morphometric assessment of the internal auditory canal (IAC) are essential to establish the anatomical bases for microsurgery of the cerebellopontine angle and acoustic neuroma, which may produce bone changes and is an important.

External ear anatomy The pinna (A), the external acoustic meatus and... Download Scientific
A trumpeted internal acoustic meatus (IAM) is an indirect sign of a vestibular schwannoma and is useful in helping to differentiate between one and other cerebellopontine angle entities, especially from a meningioma which typically does not extend into the meatus and is more often associated with hyperostosis 1.. It is characterized by widening of the medial end of the internal acoustic canal.
1 Semischematic overview of the outer (Auricula and Meatus acusticus... Download Scientific
Özocak O, Unur E, Ülger H, Ekinci N, Aycan K, Acer N. Meatus acusticus internus'un morfometrisi ve varyasyonları. Erciyes Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi. 2004;13(3) 1-7. 4. Kobayashi H, Zusho H. Measurements of internal auditory meatus by polytomography. The British Journal of Radiology 1987; 60 (711): 209-14.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/de/innerer-gehorgang-meatus-acusticus-internus/fxVF1hVVoIhH3ae4MnK7g_6DR5RNxrCV3ZH2DwqlwwQ_Meatus_acusticus_internus_02.png)
Innerer Gehörgang Anatomie und Klinik Kenhub
The internal auditory canal (IAC), also referred to as the internal acoustic meatus lies in the temporal bone and exists between the inner ear and posterior cranial fossa. It includes the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII), facial nerve (CN VII), the labyrinthine artery, and the vestibular ganglion.
Temporal Bone Anatomy
The aim of this paper was to present micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) high resolution images of the fundus of internal acoustic meatus (FIAM) and characterise the normal appearance of its singular areas which are places of passage of numerous anatomical structures. By using micro-CT we obtain detailed volume rendering images presenting topography of the FIAM in 3-dimensional (3D) space.